Some important information about the features of the airbag
The airbags will only deploy if the frontal impact of the vehicle is severe enough. The force of the impact, which causes the activation of the additional security system, approximately corresponds to a collision of a car at a speed of 40 km / h with a stationary car of the same mass and size. The airbags do not inflate in moderate frontal impacts or vehicle impacts (even very strong) rear, side, or when the vehicle rolls over.
Airbags are disposable safety devices. They are not able to protect you from repeated frontal impacts that can happen after the first impact in the same accident.
Severe injury, injury or death to the driver and passengers of the vehicle can occur in severe crashes, even if the airbags have deployed in time and the seat belts have been adjusted and fastened properly. No modern protective system can guarantee the complete safety of the driver and passengers in severe accidents.
By visual inspection of the damage sustained by the vehicle as a result of an accident, it is usually very difficult to reliably determine whether or not the airbags should have deployed. In some cases, severe damage to the body indicates that a significant part of the impact energy was absorbed by the deformation of the body elements. In this case, the deceleration threshold, to which the deceleration sensors are set and which causes the airbags to deploy, could not be exceeded. In other cases, when the impact was on a harder part of the car (e.g. running gear) and was accompanied by a more significant deceleration, the body does not receive significant visible damage, and the airbags work.
Driver airbag function
In the event of a frontal impact of sufficient force, the airbag installed in the steering wheel hub inflates almost instantly and protects the driver from hitting his head and chest against the steering wheel.
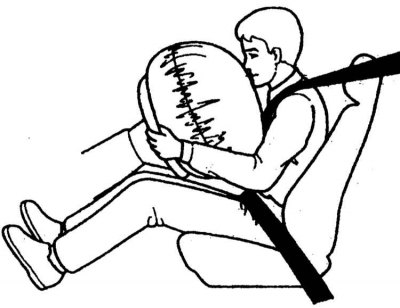
In order to effectively perform its protective function, the airbag must deploy from the collapsed state to the operational state at a very high speed. Therefore, the airbag, while protecting you from serious injuries and in some cases even saving your life, can cause minor injuries. For example, you may get scratches, abrasions on your face, etc. To reduce the risk of injury to your face from an airbag, always position yourself in the driver's seat as far away from the steering wheel as possible. At the same time, of course, you must provide yourself with a good overview and the possibility of convenient manipulation of all vehicle controls.
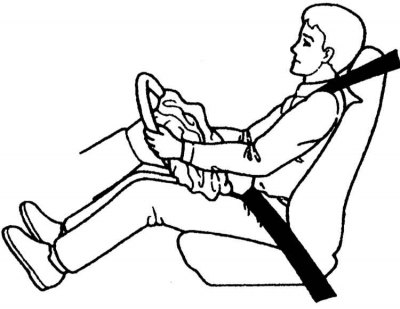
Immediately after inflating, the airbag deflates quickly, allowing the driver to visually assess the situation after a frontal impact and correct the direction of the vehicle using the steering wheel, as well as use other vehicle controls. The time interval from the moment of deployment to the deflating of the airbag lasts a fraction of a second. You may not even realize at first that the airbag has deployed.
The driver's airbag is located under the steering wheel hub cover when folded. For your safety, do not attach anything to the hub or rim of the steering wheel. These items may prevent the airbag from functioning properly or be thrown off by the inflating airbag shell and injure you or other passengers.
The passenger airbag is folded up on the top right side of the control panel under a cover labeled SRS. Do not attach any foreign objects to the cover. When the airbag deploys, these objects can be thrown away by the inflating airbag shell and injure the occupants of the vehicle.
Seat back position for safety
In order for the seat belts to perform their effective protective functions, the front seatbacks must be brought to the upright position. If you recline the seatback further, the seatbelt will not secure your body. The more the seat back is tilted back, the more likely the body is to dive under the belt in a severe frontal impact of the car and the more severe the injuries can be.
For seat back adjustment instructions, see Seat adjustment.
Head restraint position for safety
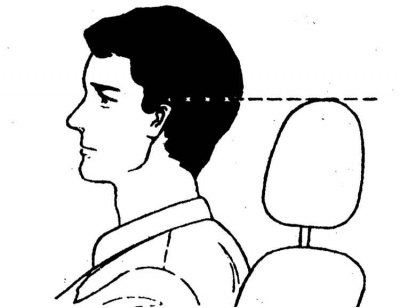
The head restraints prevent injury to the neck and head in the event of a car rear impact. The head restraint must be adjusted in height so that its top is flush with the top edge of the ear. If this cannot be achieved, the head restraint should be set to the highest position. For seat adjustment instructions, see Seat adjustment.
Keeping Children Safe
The child safety seats and cushions shown below are recommended for use in your vehicle.
 | 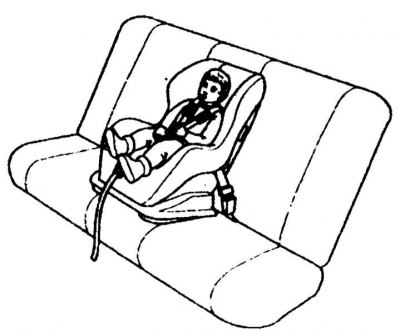 |
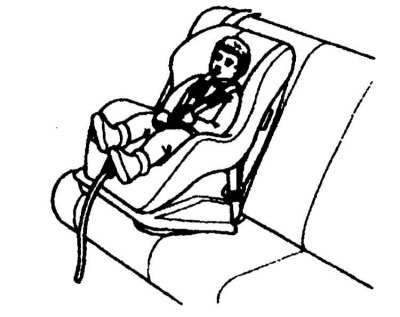 | 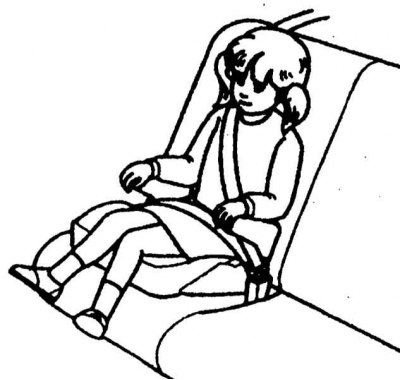 |
