Checking the starter
Note: Before starting the test, the air temperature must be between 15 and 38°C
Recommended order
- Use a starter system tester.
- Connect and use the equipment in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions.
- Perform checks as described.
Alternate order
- Use the following equipment:
- Ammeter, 0-400 A
- Voltmeter, 0-20 V (accurate to within 0.1 volt).
- Tachometer, 0-1,200 rpm.
- Connect the voltmeter and ammeter as shown.
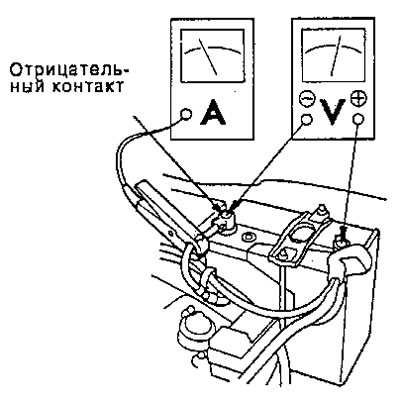
Note: After inspection or repair, reset the ECM/PCM memory to clear all fault codes.
Check that the starter turns on:
1. Remove No. 44 (15A) fuse and underhood fuse box relay.
2. Turn the ignition switch to START (III) shift lever in [N or [P] position (A/T) or neutral position (M/T) The starter should turn the engine.
- If the starter does not turn the engine, refer to step 3,
- If it cranks the engine erratically or too slowly, refer to the chapter "Check for wear and damage".
3. Check the battery, positive battery cable, ground, starter interlock relay and wire connections for looseness and corrosion, check again. If the starter still does not turn the engine, refer to step 4.
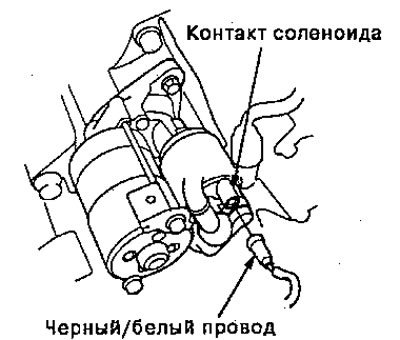
4. Pull out the connector (BLK/WHT solenoid wire and contact) from the starter.
5. Connect the connecting wire from the positive terminal of the battery [+) to solenoid contact 1. The starter should crank the engine.
- If the starter still does not turn the engine, remove it and check for problems inside the starter.
- If the starter cranks the engine, go to step 6.
6. Check the ignition switch.
7. Check the starter disable relay.
8. Check the AD transmission position indicator switch.
9. Check for an open in the wiring between the ignition switch and the starter.
10. Check the engine blocking system.
Check for wear and damage
The starter should turn the engine smoothly and steadily. If the starter turns on but cranks the engine unsteadily, remove it and inspect the starter drive gear and torque converter ring gear or flywheel for damage.
- Check the pinion overrunning clutch for binding or slippage when the rotor is rotated with the pinion gear attached.
- If damaged, replace the gear.
Check the starting voltage or starting current.
The starting voltage must be at least (*1) volt.
The starting current must be at least (*2) ampere.
*1
- Hitachi: 8.0
- Nippondenso: 8.0
- Mitsuba: 8.5
*2
- Hitachi: 200
- Nippondenso: 200
- Mitsuba: 350
If the starting voltage is too low or the starting current is too high, check for:
- The battery is damaged or weakly charged.
- Open circuit in the starting contact plate.
- Anchor jamming.
- The armature winding is closed.
- Excessive resistance in the motor.
Check RPM at startup
The engine rotation speed during startup must be above 100 rpm.
If the speed is too slow, check the following:
- Loose battery or starter contacts.
- Starter brushes are excessively worn.
- Starter contact plate circuit break.
- The helical ends or drive gear are dirty or damaged.
- The drive gear overrunning clutch is damaged.
Checking starter disconnection
When the shift lever is in [N] or [P] position (A/T) or neutral position (M/T), turn the ignition switch to START (III) and release to ON (II).
The starter drive gear should disengage from the torque converter or flywheel ring gear when you release the key.
If the drive gear meshes with the torque converter or flywheel ring gear, check the following:
- Solenoid core and switch failure.
- The drive gear assembly is dirty or the overrunning clutch is damaged
